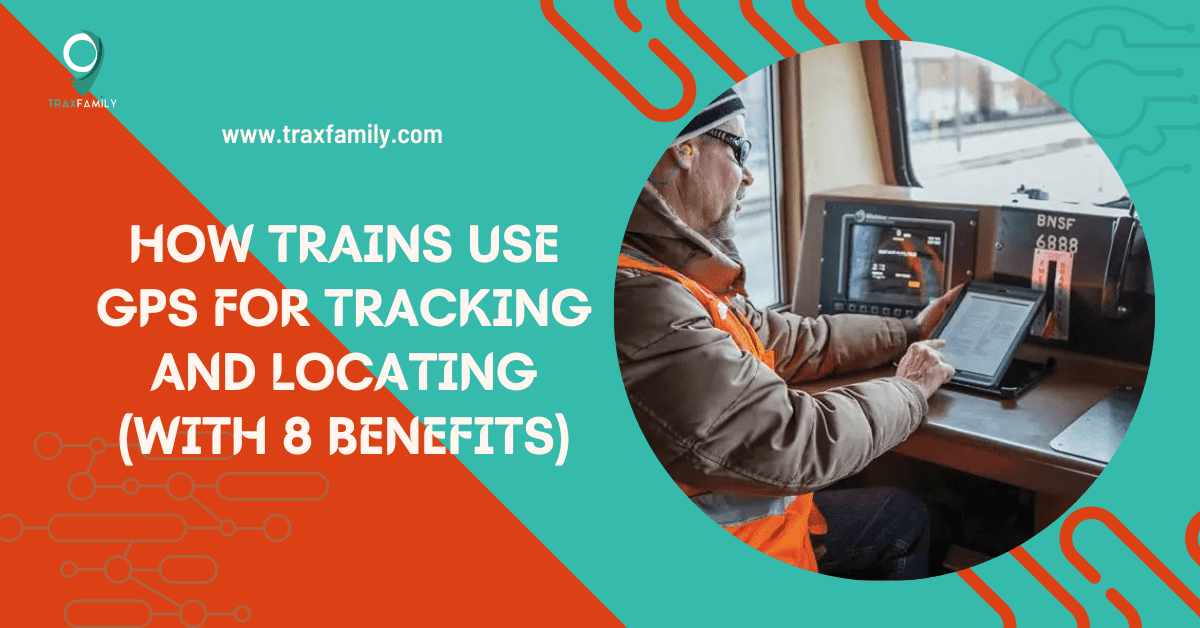
Global Positioning System (GPS) is helping major industries worldwide to increase and expand their domain. From the education sector to the farming industry, the influence of GPS has reached far and wide. The railway industry is one of them that’s reaping its yield with the help of GPS trackers.
With the advent of digital technology, railway authorities are exploiting positioning trackers to locate their vehicles in real time and maintain locomotives and wayside equipment for future use.
It’s pertinent to note that the railway positioning system offers a plethora of advantages that boost situational awareness, customer satisfaction, and cost-effectiveness.
James W. Latchford, Rail Trainmaster, shares his views, ‘Knowing the exact location of our commuter trains has been a great benefit to our riders. Each of our commuter trains is fitted with a GPS receiver and a communications system that relays our position to our Internet site on a real-time basis. From there it is available to any interested party who wants to know where the train is and when to expect it.
In the railway industry, unpredictable incidents are a part of their daily operations. With GPS, however, the authorities can prevent accidents, deploy emergency services, and serve real-time information about trains to agitated passengers.
When combined with various sensory receivers and communication systems, GPS becomes a crucial medium that improves rail security and train productivity.
How Trains Use GPS for Tracking and Locating: With 8 Benefits
The railway authorities of the United States of America adopted GPS-based Positive Train Control (PTC) systems that provide accurate information on train status and enable location mapping and automation of tracks. In the limited timeframe of 2018 to 2020, the rail tracking system has ensured safety and saved time and money.
Following are a few ways that explain how trains use GPS for tracking and locating:
1. Locates Trains

Trains are a crucial means of transport across the U.S. They are responsible for carrying an immense load of valuable cargo. According to PopSci, freight railroads are the future of the American shipping industry. Their estimate says in 2013, the freight trains transported almost $50 billion worth of goods in the United States every day.
Tracking trains using GPS is crucial because of various reasons. The trains can get derailed or even delayed in reaching their destination if they face technical difficulties or breakdown in the middle of their journey.
Another possibility could be when the train temporarily loses its way due to low visibility, inclement weather, or unpredictable natural calamities. Such situations often leave the rail cars stranded in remote locations. Combat such a situation using a robust and efficient GPS train tracking device.
Over the years, the number of train mishaps has increased drastically. Thus, it becomes inevitable to keep track of these vehicles and their routes via GPS trackers. The U.S. Department of Transportation Federal Railroad Administration has examined the viability and effectiveness of the High Accuracy Nationwide Differential Global Positioning System. It’s an advanced version of the traditional GPS that provides accurate location of trains.
When the rail car operator has sufficient information about the location and status of the train, it helps them to make intelligent and rapid decisions. Moreover, the positioning data alerts the operator about the train speed details. These details help them diagnose possible safety issues and take impactful measures to bring the vehicle back to safety.
2. Decreases Train Stopping Distance
Unlike most vehicles, trains have longer braking distances. The braking distance is the length a vehicle travels once the driver has pulled the brakes and until it finally stops.
Trains are harder to stop. It’s because of the mass of the train, which is more than a car and therefore requires massive force when it’s in motion.
In the case of trains, be they passenger trains or freight cargo, they travel 250 m at a speed of 100 mph before coming to a stop. Stopping a freight cargo carrying heavy materials in the middle of its track is challenging for the driver. Also, the longer a train takes to stop, the more likely the brakes will overheat. Sometimes, you might have to replace them.
According to Minnesota Operation Lifesaver, a freight cargo requires ‘a mile or more to stop.’ Likewise, heavier locomotives have longer stopping distances. The distance will lengthen if the vehicle is moving at a faster speed.
When such a situation occurs, the GPS can help trains reduce their long braking distances by sending real-time information about traffic patterns and other obstacles. That way, the train doesn’t have to stop in its tracks. Instead, the driver receives the signals and takes routes free from traffic to get back on schedule.
When trains get stranded in foreign lands, the crew and the passengers can be in danger. Several incidents occurred in the past when a train’s long braking distances led to severe catastrophes. Robbers from nearby areas could be on the lookout and attack innocent passengers and crew members.
Avoid such instances with a GPS tracking system that continuously feeds the computers and the authorities with information about the train’s location and speed. Furthermore, they would inform them of the track conditions ahead.
3. Empowers Train Tracker Maps
The advancement in GPS technology has allowed trainspotters to keep track of trains via several GPS-based mobile applications. Gone are those days when the trainspotters, or people who devote their time to locating trains, would use printed schedules and time charts to assume the location of trains.
Instead, the community of train enthusiasts uses power train tracking maps like the Track Trace Train Radar application.
The historical community of train enthusiasts has interactive forums where they share photographs of trains in action. With a rail GPS positioning system, the trainspotters can accurately predict where the train is stationed at a particular point of the day.
It further alerts them when a train will pass by their nearest station. That way, they have the opportunity to catch their trains in action.
4. Prevents Disasters
In 2008, the Metrolink disaster killed 25 passengers and injured more than a hundred. It occurred when a Metrolink commuter train collided with a Union Pacific freight train in Los Angeles. This gruesome incident stimulated the U.S. congress to bring about a bill that encouraged GPS tracking in the rail industry.
That same year, the U.S. Government mandated the application of Precision Train Control (PTC) by enhancing the existing GPS. They optimized the tracking technology to meet the Rail Safety Improvement Act of 2008.
With the conventional rail GPS tracking system, minor errors cropped up because of disturbing weather conditions, and miscalculations led to further problems. However, PCT technology tackles these erroneous readings using the Nationwide Differential GPS (NDGPS). It’s a network of ground-based reference stations.
The technology signals the train controller, giving them information about the train’s current location and the railroads it’s traversing in a language popular among the rail industry. If the GPS senses any disturbance ahead, the sensory receiver alerts the controller about the potential danger.
Further on, the onboard computers receive the data from GPS and use them automatically to control or monitor the train’s movement. It has proven beneficial in preventing unsafe movement and tabulating the vehicle’s real-time location.
With NDGPS, the train operator can re-route traffic and avoid areas with poor satellite signals, like tunnels. Also, PTC technology can direct the maintenance crews about when to get on and off the track.
5. Improves Visibility

Often, trains have to traverse areas of low visibility due to fog, rain, or other troublesome weather conditions. In such situations, there’s a possibility that trains might collide with each other, causing massive destruction and even death. GPS helps prevent such casualties by alerting the driver of an approaching train on the same track or diverting the train to a safe rail track.
The visibility of the rail authority limits not only to natural conditions, but GPS encourages transparency and clarity regarding shipping management.
Rail GPS tracking devices improve clarity by sending their real-time location to the authorities via a map tracking system. It alerts the rail companies of the reasons behind a train’s delay, the delivery status of cargo, location of the train crew and drivers.
GPS’ caliber doesn’t end at providing real-time location of the rail car. It further expands its focus and helps authorities ensure the carriage is safe and the goods are carefully stored. If a product goes missing, the rail authorities can easily track it using GPS tags.
Once the goods are delivered or have reached their destination, the manager responsible for cargo receives a push message. This kind of clarity in shipping management increases productivity and security. It elevates the quality of product delivery. GPS trackers, therefore, allow cargo managers to ensure the goods reach their owners on time, and the increased visibility helps them make effective decisions when required.
6. Supervises Cargo Condition
Not all shipment goods have longer storage life; some are perishable and only stay fresh for a short period. Hence, they require optimum storage conditions to maintain quality throughout the journey. With GPS trackers, cargo managers can place GPS tags on egg crates or milk barrels and monitor their storage condition.
GPS tracks the humidity of the storage area and records the shock and vibration level a product experiences throughout the journey. If there’s even a single-degree drop in temperature, the GPS alerts the manager of this change, and the crew immediately fixes the setting.
Furthermore, it provides specific insights if any damage is about to occur, alerts authorities about replacement requirements, and informs customers about changes in plans or timing immediately. Also, the tracking system streamlines the authorities’ attention to the site of damage and schedules a map for the train’s future reference.
7. Reduces Cost

Dr. Paul E. Firmin, a professor at the University of Leeds Institute of Transport Studies, mentions in his 2006 research paper that satellite navigation systems will reduce rail and fleet management costs. Supportive studies have further shown that GPS tracking systems offer alternative and better route options that cut fuel consumption.
When the train controller chooses the shortest distance, they save time, fuel, and money. In addition, the train journey is smooth and efficient. Subsequently, the driver spends less time on the road, the cargo gets delivered faster, and the company has to bear lesser fuel expenses.
8. Prevents Theft
Besides preventing theft, GPS warns the train controllers about potential theft situations. It’s helping large conglomerates to reduce the theft of property and goods. Rail car GPS trackers enable rail authorities to undertake precautionary steps for a small investment. Such measures prevent criminal attempts at stealing goods.
The rail administration uses the geofence feature of the train GPS tracker to identify a territory under surveillance. The tracker readily alerts the cargo manager when the goods or products containing the device tag are removed from their safe zone or after business hours. It ensures the security of the goods, and the administration doesn’t waste time tracking the goods and the perpetrator.
Similarly, the mechanism alerts the rail authority when the train deviates from its prescribed route or signals to them about the timing of the train leaving and entering the rail yards.
Also, the operators can customize the rail GPS tracking system to detect and inform whenever tampering occurs. They can further optimize the tracking system in such a way that it maintains security even if the device tags are compromised.
Conclusion
Over the years, the rail industry has transformed and optimized its functional mechanism to improve operational effectiveness and passenger safety and security. With PTC’s advanced technology, rail authorities can now prevent train-to-train collisions and derailments because of high-speeding vehicles and monitor the movement of the trains by placing a mainline switch in the proper position.
The GPS technology will further refurbish the railway industry with efficiency and sustainability. Researchers are studying ways to upgrade GPS trackers to support communication between two vehicles. Such a communication system will help avoid collisions and accidents at railroad crossings.
GPS is an integral part of the rail industry, which makes a conductor or operator’s job easier. This further broadens the success rate of private rail companies that can exploit GPS trackers to ensure security and productivity.
Also Read About: Benefits of GPS In Farming And Agriculture

Stefan Quartemont is an experienced author and expert on GPS technology, with a particular interest in its practical applications. He gained his knowledge of GPS tracking during his studies at Texas A&M University and has since become a regular contributor to TraxFamily.com, providing valuable insights into the latest developments in GPS tracking. Stefan’s expertise and passion for leadership make him a respected authority on GPS technology, and his work with TraxFamily.com is highly beneficial to anyone interested in staying up-to-date on this exciting technology.